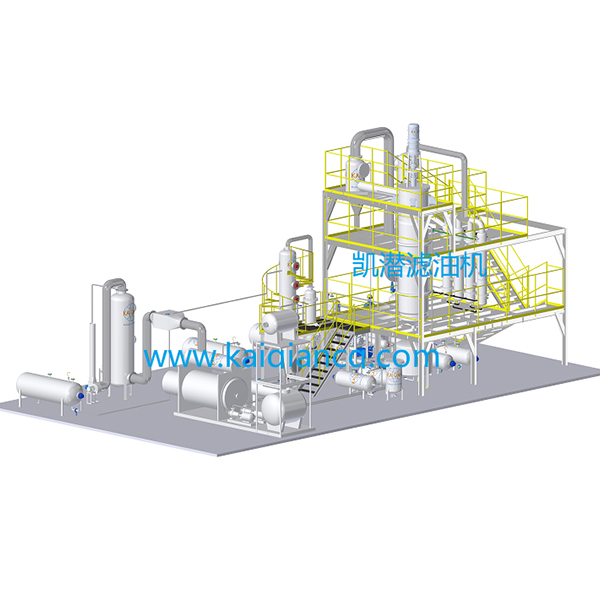
How to Purify Used Engine Oil?
Writer: Kaiqian Oil Purifier Release time:2024-06-18 17:09 Clicks:
Engine oil is essential for the operation of internal combustion engines as it lubricates moving parts, reduces friction, and helps keep the engine cool.
Over time, engine oil accumulates contaminants such as dirt, metal particles, and combustion by-products, which diminish its effectiveness.
Instead of discarding used engine oil, purifying and recycling it can be both environmentally friendly and cost-effective. This article explores the various methods and processes involved in purifying used engine oil.
Understanding the Contaminants
Before diving into the purification process, it's essential to understand the types of contaminants that need to be removed from used engine oil. These contaminants typically include:
Particulate Matter: Dust, dirt, and metal particles from engine wear.
Water and Coolant: Moisture from condensation and coolant leaks.
Oxidation Products: Varnish and sludge are formed due to oil oxidation.
Chemical Contaminants: Fuel residues, acids, and other chemical compounds.
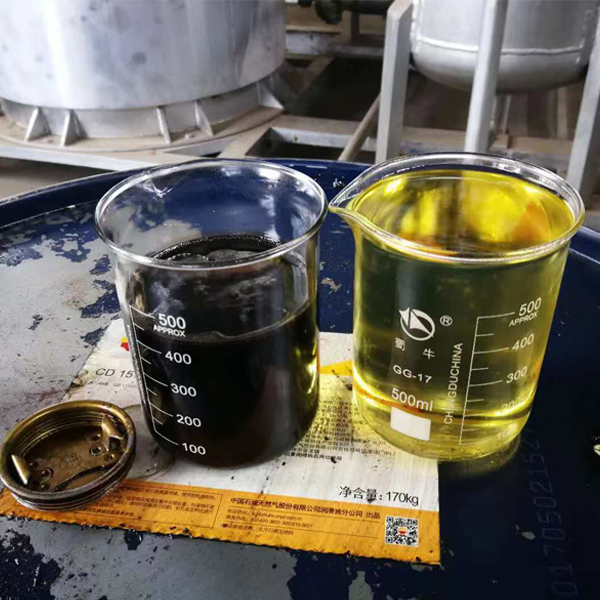


The Importance of Purifying Used Engine Oil
Purifying used engine oil offers several significant benefits:
Environmental Protection: Properly disposing of or recycling used oil prevents soil and water contamination.
Resource Conservation: Recycling oil reduces the demand for new oil production, conserving natural resources.
Economic Savings: Recycled oil can be re-refined and reused, reducing the need to purchasenew oil.
Methods of Purifying Used Engine Oil
Several methods can be employed to purify used engine oil. These methods range from simple filtration processes to more complex chemical treatments.
1. Filtration
Filtration is one of the most straightforward methods for removing solid particles from used engine oil. This process involves passing the oil through a filter medium that traps contaminants while allowing the clean oil to pass through.
Types of Filtration
Simple Filtration: Using standard oil filters to remove large particles.
Centrifugal Filtration: Utilizing centrifugal force to separate particles based on their density.
Vacuum Filtration: Employing a vacuum to pull oil through fine filters, capturing smaller particles.
2. Sedimentation
Sedimentation relies on gravity to separate heavier particles from the oil. The used oil is allowed to sit undisturbed in a container, enabling the denser particles to settle at the bottom. This method, while simple, is often used in conjunction with other purification techniques to improve efficiency.
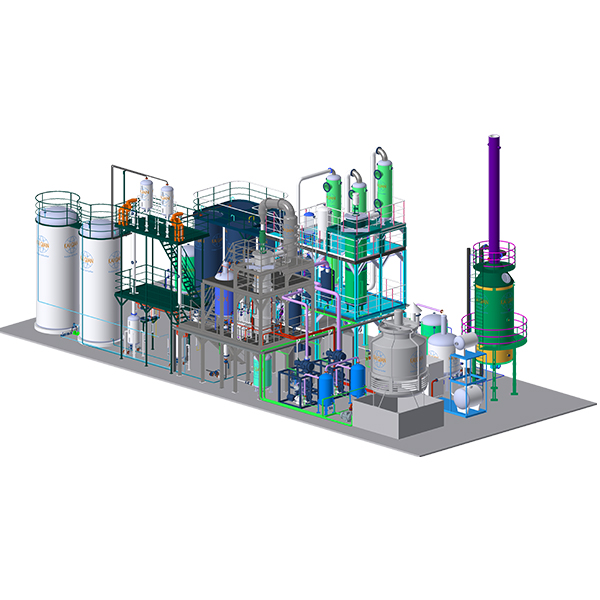

3. Distillation
Distillation involves heating the used oil to vaporize it and then condensing the vapor back into liquid form. This process can effectively remove water, light hydrocarbons, and other volatile contaminants.
Steps in Distillation
Heating: The used oil is heated in a distillation column.
Vaporization: Contaminants with lower boiling points vaporize first.
Condensation: The vapor is cooled and condensed back into a purified liquid.
4. Chemical Treatment
Chemical treatment involves adding specific chemicals to the used oil to neutralize or remove contaminants. Common chemicals used include acids, alkalis, and coagulants.
Types of Chemical Treatments
Acid-Base Neutralization: Neutralizing acidic or basic contaminants with corresponding chemicals.
Coagulation: Adding coagulants to aggregate fine particles into larger clumps, which can then be filtered out.
Clay Treatment: Using activated clay to adsorb impurities and contaminants from the oil.
5. Vacuum Distillation
Vacuum distillation is a more advanced form of distillation performed under reduced pressure. This method lowers the boiling point of the oil, allowing it to be distilled at lower temperatures, which prevents thermal degradation of the oil.
Advantages of Vacuum Distillation

6. Hydrotreating
Hydrotreating is a refining process that uses hydrogen gas to remove impurities such as sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen compounds from the used oil. The process also saturates unsaturated hydrocarbons, improving the stability and performance of the recycled oil.
Process of Hydrotreating
Hydrogen Addition: Hydrogen gas is mixed with the used oil.
Catalytic Reaction: The mixture passes over a catalyst bed, promoting chemical reactions that remove impurities.
Separation: The purified oil is separated from the reaction by-products.
7. Ultrafiltration
Ultrafiltration utilizes a semi-permeable membrane to separate fine particles, emulsified water, and other contaminants from the used oil. The membrane allows only clean oil molecules to pass through, blocking larger impurities.
Benefits of Ultrafiltration
Combining Methods for Optimal Results
While each of these methods can be used individually, combining them often yields the best results. For example, a multi-stage process might involve sedimentation to remove heavy particles, followed by filtration to capture finer particles, and then chemical treatment to neutralize remaining contaminants.
Example of a Multi-Stage Purification Process
Pre-treatment involves sedimentation to settle heavy particles.
Filtration: Centrifugal filtration is used to remove large solids.
Chemical Treatment: Adding coagulants to aggregate fine particles.
Vacuum distillation is a process used to remove water and volatile impurities.
Final Filtration: Ultrafiltration is used to ensure high purity.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
When purifying used engine oil, it is crucial to consider safety and environmental factors:
Handling Chemicals: Ensure proper handling and storage of chemicals used in the purification process to prevent accidents and spills.
Waste Disposal: Dispose of waste materials, such as sludge and spent filters, according to local regulations to minimize environmental impact.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use appropriate PPE, such as gloves and goggles, to protect against exposure to hazardous substances.
Conclusion
Purifying used engine oil is a valuable practice that contributes to environmental protection, resource conservation, and economic savings.
Various methods, ranging from simple filtration to advanced chemical treatments and vacuum distillation, can be employed to remove contaminants and restore the oil's effectiveness.
By understanding and implementing these purification techniques, individuals and industries can play crucial roles in promoting sustainable practices and reducing the ecological footprint of engine oil usage.

 简体中文
简体中文
 English
English
 Français
Français
 Русский язык
Русский язык
 Polski
Polski
 日本語
日本語
 ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Português
Português
 español
español
 Italiano
Italiano
 한어
한어
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
 Pilipino
Pilipino
 بالعربية
بالعربية
 বাংলা
বাংলা
 IndonesiaName
IndonesiaName
 ກະຣຸນາ
ກະຣຸນາ
 Türkçe
Türkçe
 简体中文
简体中文
 English
English
 Français
Français
 Русский язык
Русский язык
 Polski
Polski
 日本語
日本語
 ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Português
Português
 español
español
 Italiano
Italiano
 한어
한어
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
 Pilipino
Pilipino
 بالعربية
بالعربية
 বাংলা
বাংলা
 IndonesiaName
IndonesiaName
 ກະຣຸນາ
ກະຣຸນາ
 Türkçe
Türkçe